Carbon nanodots (CNDs) are quasi-spherical nanoparticles with size below 10 nm, typically made of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms. CNDs have attracted a lot of attention, due to their benign, abundant and inexpensive nature.Especially their intriguing photoluminescence (PL) properties have brought them the label of "carbon nanolights".
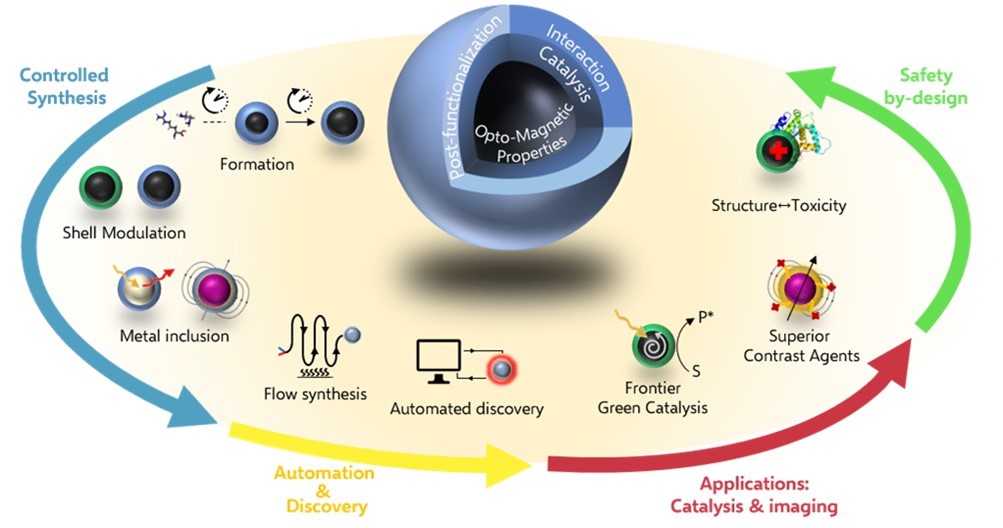
In the frame of the ERC Advanced Grant "e-DOTS", the Carbon Nanobiotechnology laboratory started a new research program, where the main objective is to produce tailored CNDs with full control of their chemical, electrochemical and photophysical properties. The structural and molecular control of the CND core and their surface functionalities will enable their implementation into functional materials and devices (Fig. 1). Tailored CNDs will serve as safe and high-quality bioimaging platforms, as well as green and effective catalysts for advanced transformations in water.
The e-DOTS project takes advantage of nanoscale and process-intensification principles, information technology and automation/robotics to translate molecular properties to nanoparticles, for use in technologically advanced challenges, ranging from high quality bioimaging to green catalysis in water. A stringent molecular control over the synthesis and multivalent properties of "carbon nanodots", 2-5 nm spherical nanoparticles, will allow us to shape a nanofabrication space with engineered functions. The core-shell structure of carbon nanodots, consisting of a confined core and an outer functional shell, can be rationally designed by controlled chemical approaches and by a tailored choice of the proper starting materials. e-DOTS scientific objectives are planned to go beyond the state of the art, with the aim to: (i) elucidate the mechanism and the structural details in the conversion of small molecules to nanoparticles; (ii) expand the carbon nanodots preparation process window and allow its automated exploration, directed at ambitious targets; (iii) design and prepare carbon nanodots with tailored properties - in terms of size, charge, luminescence, chirality, and outer-shell functions – outperforming current technologies in green catalysis and biomedical imaging. (iv) investigate and ensure the safety profile of carbon nanodots in a safe-by-design approach. e-DOTS is a highly interdisciplinary project, based on frontier methods that the Prato group has successfully designed for the molecular modification of very diverse carbon nanostructures. Delving into fundamental aspects of carbon nanodots will allow to unfold their full potential in technological and biological applications. e-DOTS will thus offer unprecedented opportunities to the scientific community, since the specific molecular properties of the reactants can be transferred, combined and enhanced up to the nanoscale, yielding carbon nanodots tailored to function.