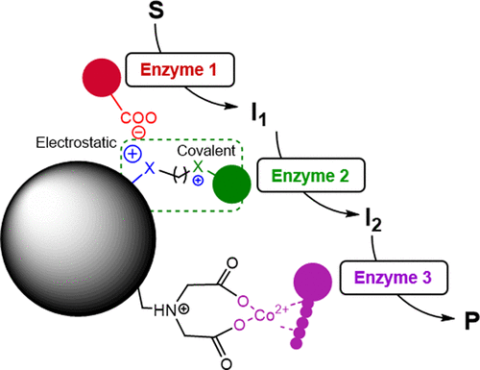
Immobilized multienzyme systems are gaining momentum in applied biocatalysis; however, the coimmobilization of several enzymes on one carrier is still challenging. In this work, we exploited a heterofunctional support activated with three different chemical functionalities to immobilize a wide variety of different enzymes. This support is based on agarose microbeads activated with aldehyde, amino, and cobalt chelate moieties that allow a fast and irreversible immobilization of enzymes, enhancing the thermostability of most of the heterogeneous biocatalysts (up to 21-fold higher than the soluble one). Furthermore, this trifunctional support serves to efficiently coimmobilize a multienzyme system composed of an alcohol dehydrogenase, a reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) oxidase, and a catalase. The confined multienzymatic system demonstrates higher performance than its free counterpart, achieving a total turnover number (TTN) of 1 × 105 during five batch consecutive cycles. We envision this solid material as a platform for coimmobilizing multienzyme systems with enhanced properties to catalyze stepwise biotransformations.
DOI: 10.1021/acs.biomac.2c01364
KEYWORDS: Aldehydes,Immobilization, Organic polymers, Peptides and proteins, Sodium